Nuclear power plants: how dangerous is the attack, and what are the risks in Ukraine?
Written byTimes Magazine

What happened to the power plant?
Russia opened fire on Zaporozhye and then took over the facility. According to a Ukrainian nuclear inspection, buildings around one of the six power plants were damaged. However, the United Nations atomic regulator, the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA), said no plant safety systems were affected, and no radioactive material was released.
Damage to the reactor the device that generates energy in a nuclear power plant and the building that houses it can cause the reactor to overheat and melt its core.
The radiation can then escape into the environment. If people are exposed to this radiation, it can have severe immediate and long-term health effects, including cancer.
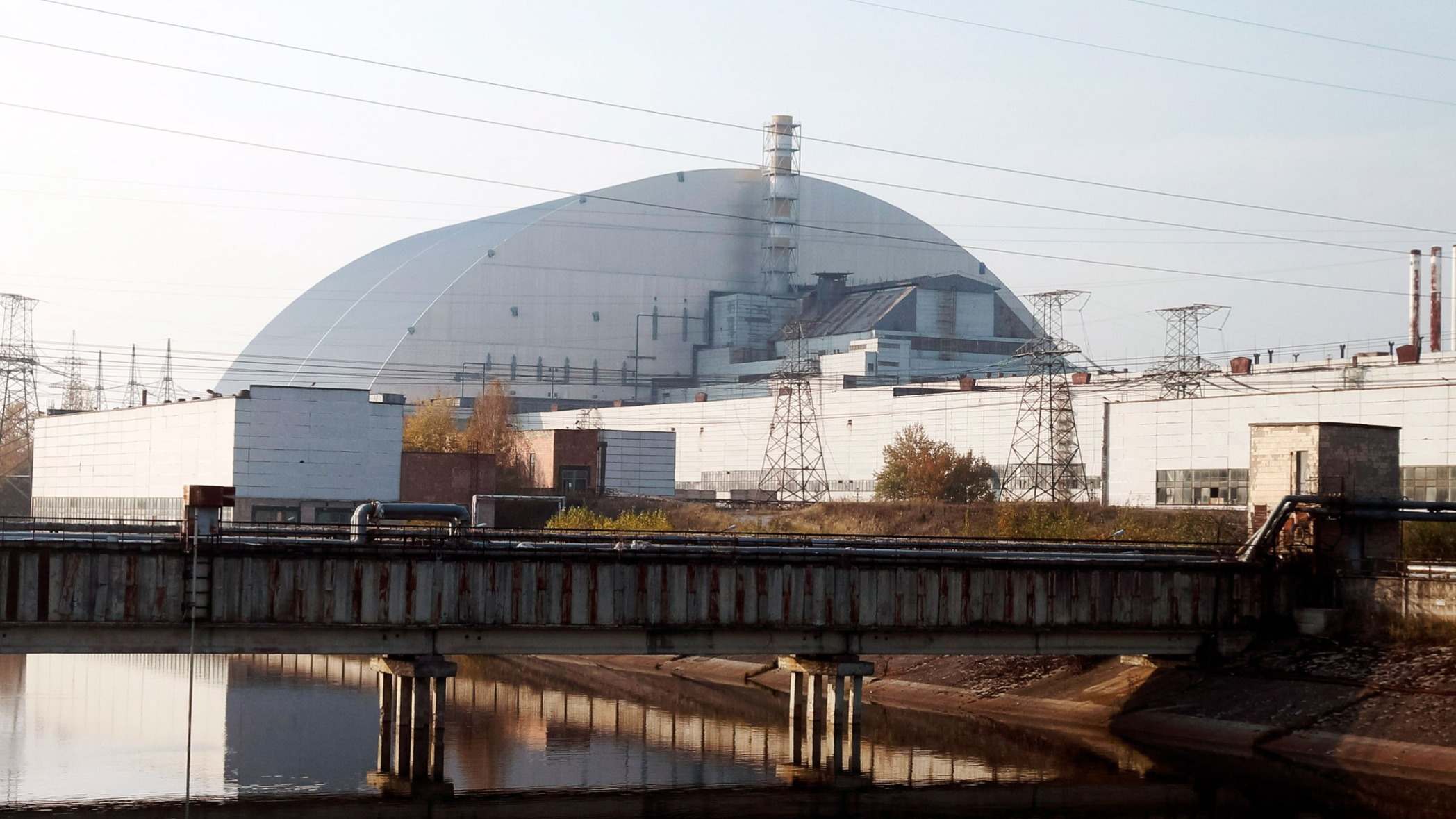
Could that attack be "another Chernobyl"?
Experts say although the attack is dangerous, there are essential differences between Chernobyl and Zaporozhye .According to Mark Wenman from Imperial College London, the Zaporozhye location is much safer.
He said the reactor was housed in a reinforced concrete building that "can withstand extreme external events, both natural and man-made, such as a plane crash or explosion." Also, the Zaporizhzhya plant does not contain graphite in its reactor. At Chernobyl, graphite caused significant fires and was the source of the radiation trail that ripped through Europe.
What happens if a nuclear power plant fails?
"You don't have to hit a factory directly to get into trouble," said Oleksiy Pasyuk, deputy director of Ecoaction, an energy advocacy group in Ukraine. Interruptions to the power supply to the facility can also cause serious problems.
The Ukrainian side is in the process of shutting down the reactor for protection. It is now believed that only one of the six reactors in operation at the power plant is operational. However, the reactor cannot simply be turned off like a conventional power supply. Instead, they must be cooled slowly for 30 hours, which requires a constant power supply to the facility.
Disruption of this energy supply and thus the cooling process can also cause radiation losses. This can happen if nuclear fuel exceeds its melting point and radioactive material penetrates a containment facility.
Trending News